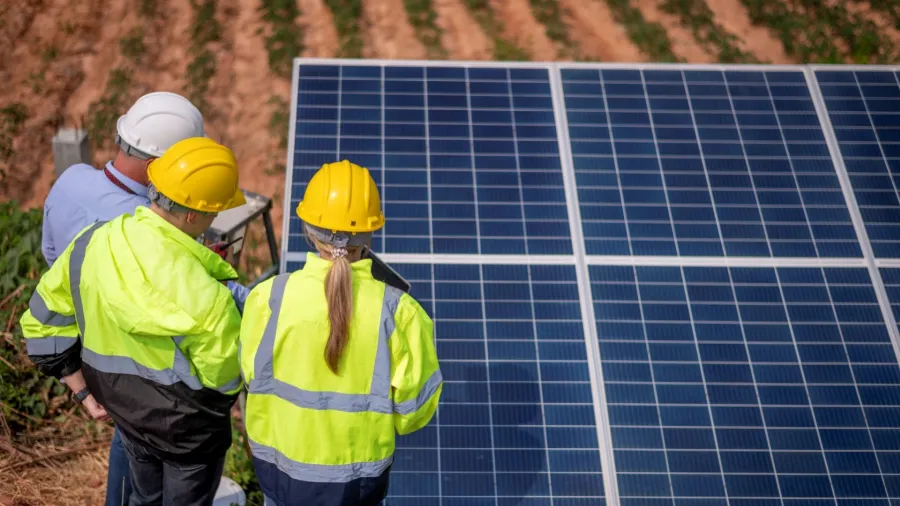
Aon launches low carbon framework to guide insurers in energy transition
Battery energy storage systems are expected to generate over $1b in GWP by 2027.
Aon has introduced a Low-Carbon Transition Framework for insurers as the firm aims to help (re)insurers capture growing premium opportunities in the sustainable energy sector, which is forecast to generate more than $9b in global premiums by 2030.
The new framework sets out a seven-step process that focuses on strategy, evaluation, innovation and talent. It aims to help (re)insurers align underwriting appetite with emerging technologies, manage transition risks and use analytics to benchmark portfolios.
Aon said the approach allows companies to assess current exposures, define strategy and identify areas for growth.
Aon’s research points to strong premium growth across the energy transition segment, driven by demand for insurance products that support clean-energy projects.
Battery energy storage systems are expected to generate more than $1b in GWP by 2027, supported by an estimated 25% compound annual growth rate linked to needs for embedded cover and cyber protection.
Hydrogen-related risks could represent $5b in GWP by 2027 with growth of at least 10%, while insurance for renewable power generation is projected to rise by almost $3b between 2024 and 2030.
Aon said talent and product development will be central to capturing this growth.
Its Power, Utility and Renewables team is developing solutions such as parametric weather cover and forced-outage programmes designed to improve the feasibility of renewable and low-carbon projects.
Proprietary tools, including Aon’s Global Power Premiums data and Transition Performance Index, are being used to track sector trends, claims and loss ratios to support pricing and risk selection.















 Advertise
Advertise